
[ad_1]
Non-Fungible Tokens(NFTs) are now becoming increasingly popular among crypto enthusiasts and, recently, even among non-blockchain enthusiasts. Social media sites are integrating NFT art into their applications, Hollywood stars are launching their own collection, and big tech giants are exploring the potential of these digital identifiers.
This much fanfare comes with its own set of risks. As the popularity of NFTs surges, so do NFT scams. One such prominent scam is NFT wash Trading. NFT Wash Trading, in short, is a method of market manipulation through which a trader buys and sells the same securities many times in a short period to inflate the asset’s price.
Before 2022, wash trades rarely accounted for over 10% of the volume, but with 2022, NFT wash Trading has spiked to concerning rates. According to a recent Dune report, around 60% of NFT trading volumes in 2022 were wash trades.
Earlier this year, a Chainalysis report also disclosed that around 110 wash trading addresses had generated $8.9 million in profit. The report further revealed that wash trading and money laundering through the purchase of NFTs were the two most common activities related to NFTs scams.
These concerning stats makes it much more imperative for every crypto enthusiast to educate themselves on the fraud that Wash Trading is. So Let’s Dive In!
How does NFT Wash Trading Work?
Wash Trading happens when a trader buys or sells securities with the sole intention of increasing the crypto asset’s trade volume by creating the illusion that the asset is worth more than its “real” value.
Usually, in all major NFT marketplaces, a user can control both sides of an NFT trade, selling the NFT from one wallet and also purchasing it from another. This makes it much for easier for traders to engage in wash trading. The trader can set up multiple accounts on the marketplace and use them to buy and sell the NFT back and forth. On a smart contract level, the same wallet address may be the buyer as well as the seller of an NFT.
The trade volume spikes when the user starts buying and selling the securities multiple times. This makes the underlying asset seem highly sought after, eventually leading to price inflation.
NFT owners are now readily participating in wash trading to lure impressionable purchasers into buying the NFT at an exorbitant price. Reportedly, platforms rewarding users for executing trades were the most exploited as they have incentivized more people to try wash trading.
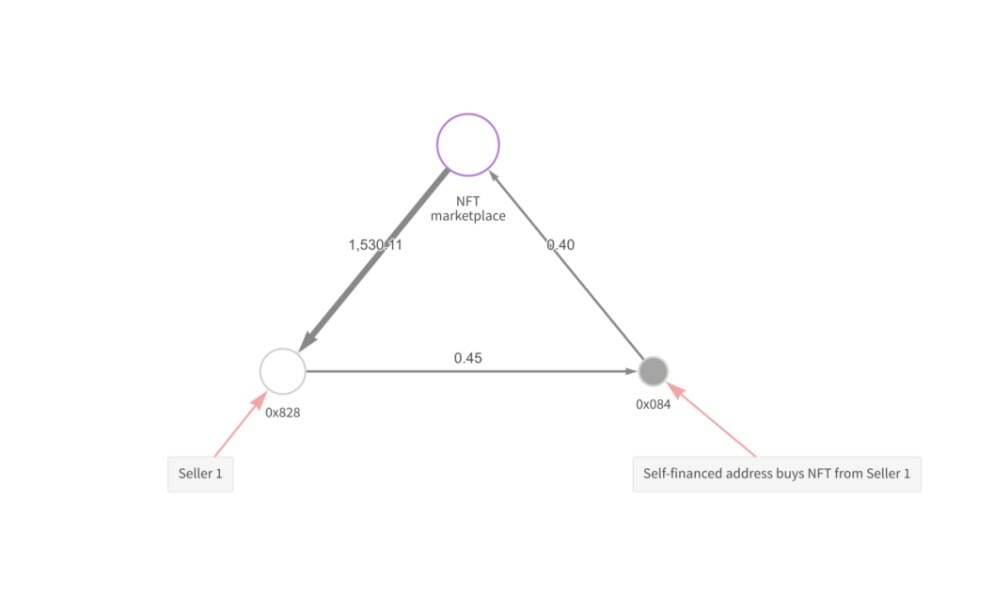
The most common wash trading methods involve investors trading their NFTs between two or more wallets, which they control, for the highest amount of Ether possible. They do this solely to accumulate token rewards more valuable than the gas fees spent.
Another symptom of wash trading is previous crypto transfers from the selling wallet to the purchasing wallet, indicating the sale is self-funded.
Keeping Yourself Safe
Experts believe wash trading is likely to become more common in the days to come. Research and basic knowledge of NFT trading are all you need to keep yourself safe from this scam. Get ahead of scams by reading up on them and how they work. Doing so should give you an idea of what to avoid and watch out for.
To easily spot wash trading, one has to look for the same wallet addresses popping up in an asset’s history. Tools like Etherscan and BscScan can be used to show the wallets that have previously owned an NFT.
NFT Marketplaces should also take a proactive approach to prevent wash trading. They could do so by introducing bans/penalties on users who sell NFTs to addresses they’ve self-financed. For e.g., OpenSea-the world’s largest NFT Marketplace recently created a private NFT security group, where users will collaborate to raise scam concerns to companies and Web3 ecosystems.
NFT scams will continue to plague the Web3 space if users don’t stay informed and vigilant. So we request you invest the time and resources needed to prevent falling prey to scams.
[ad_2]
Source link





